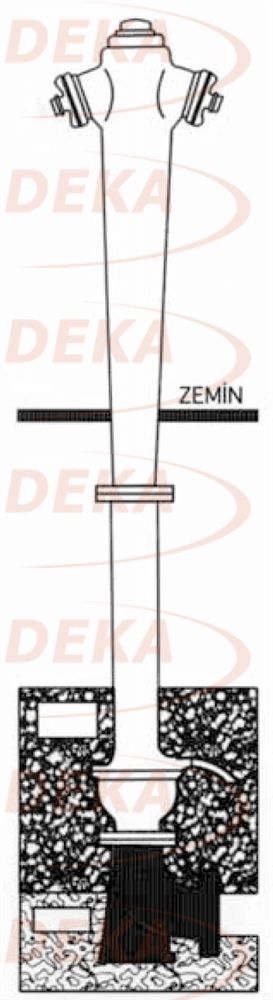
In accordance with the Regulation on the Protection of Buildings from Fire, an external hydrant system is compulsory if the floor areas of the buildings with all kinds of usage and planned to be built separately from the general residential areas are larger than 5000 m2.
It is used to protect fires from fire with hydrants and to intervene fires that cannot be extinguished during the first intervention. Fire hydrant lines should cover the entire perimeter of the building or building as much as possible.
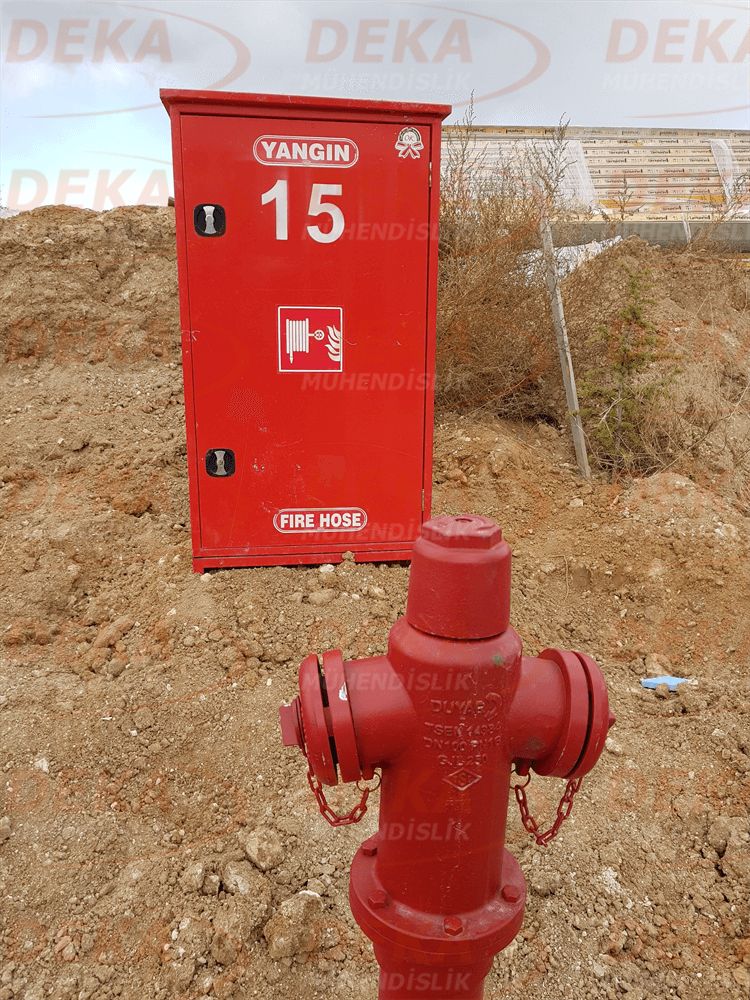
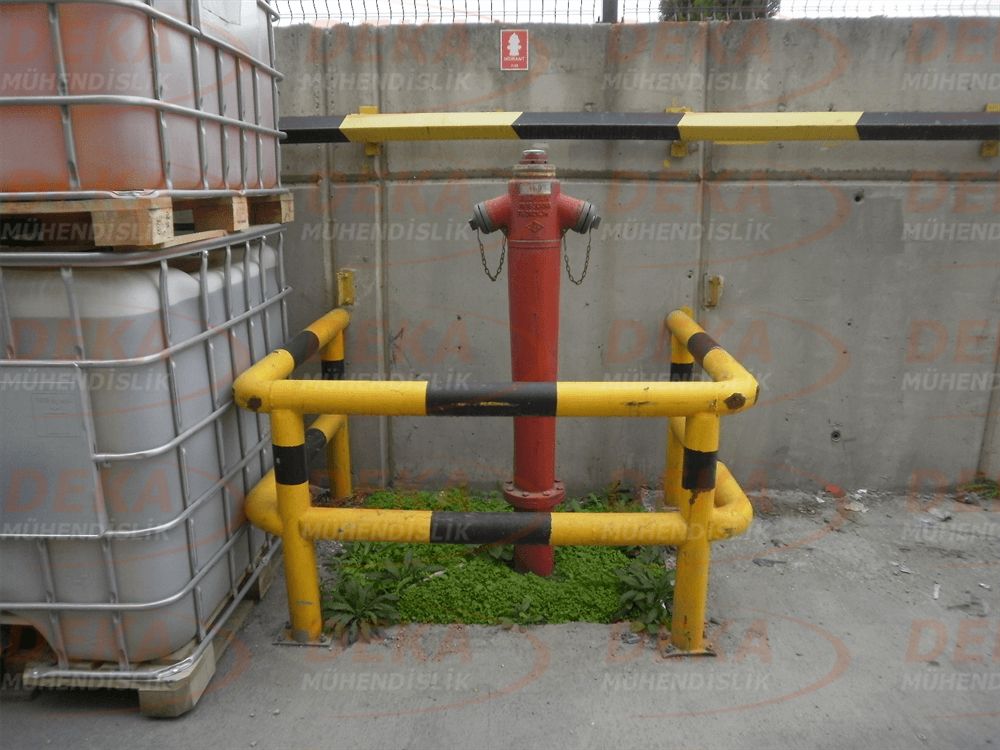
Fire hydrants are arranged in such a way that firefighters and their vehicles can easily reach and connect.
Hydrant system design flow is determined according to the applied system, building hazard class and application. The distance between hydrants is taken as 50 m in very risky areas, 100 m in risky areas, 125 m in moderate risk areas and 150 m in low risk areas, according to local authorities. In practice, we recommend placing it at intervals of 50 m so that there is no space where no outdoor fire hydrant is applied.
In order to ensure safe and most beneficial use from fire hydrants, the distance to the building is determined as minimum 5m and maximum 15m.
We determine the pipe diameter that supplies the water to the fire hydrant system with the hydraulic calculation program. If there is no ring system in the hydrant system, the diameter of the lowest pipe that can be used is 100 mm and is determined according to the hydraulic calculation.
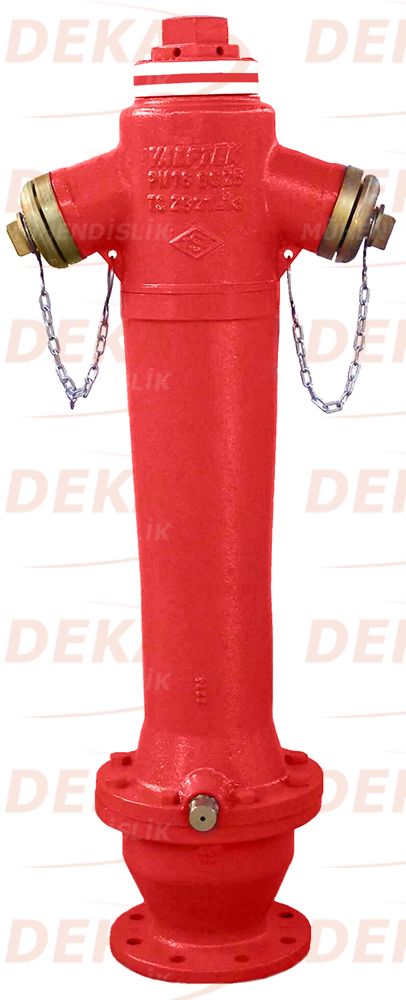
Fire hydrants are required to comply with the relevant Turkish Standards.
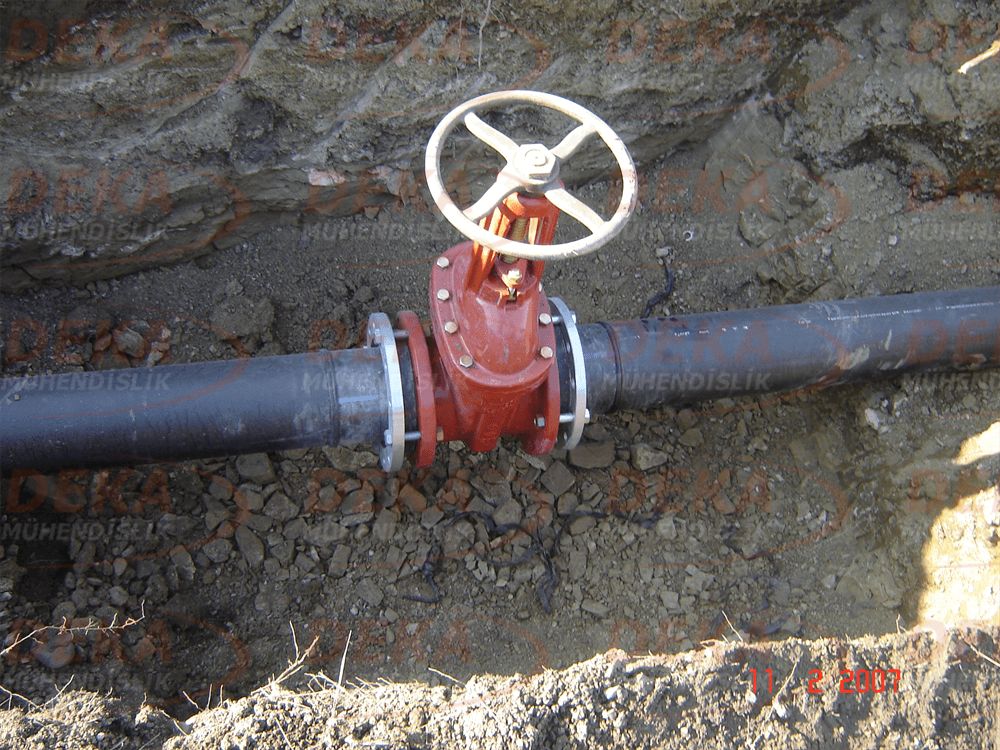
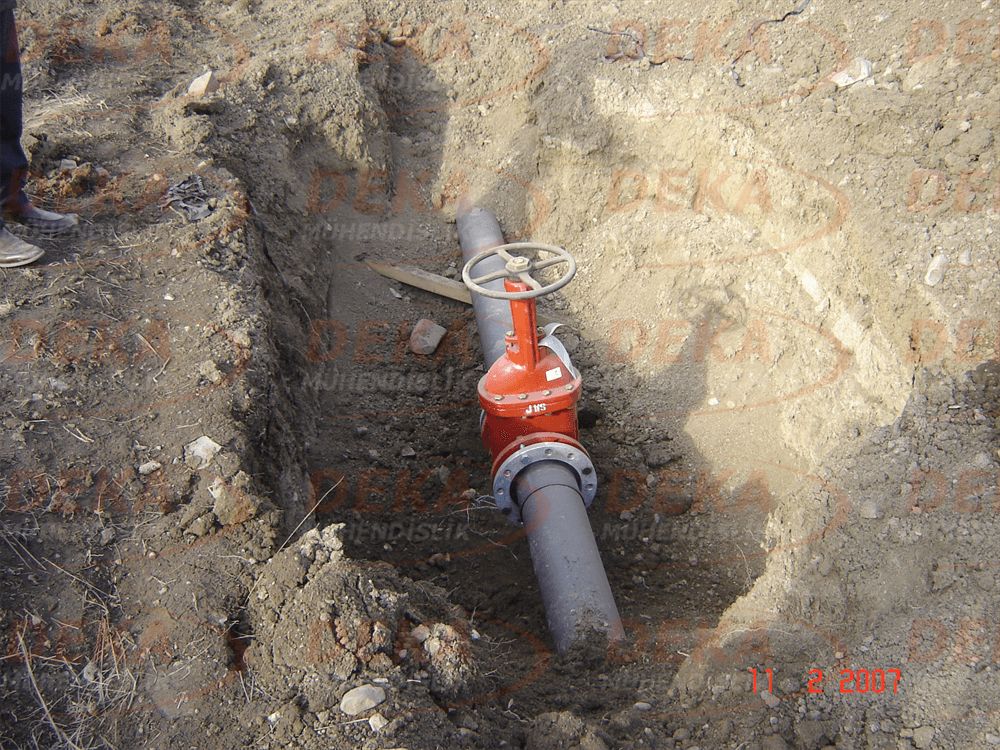
Considering the risk area in the hydrant system, 1 isolating valve and water discharge system should be installed in an average of 5 equipment. Thus, the facility / building does not remain unprotected surface during possible damage, maintenance and overhaul work.
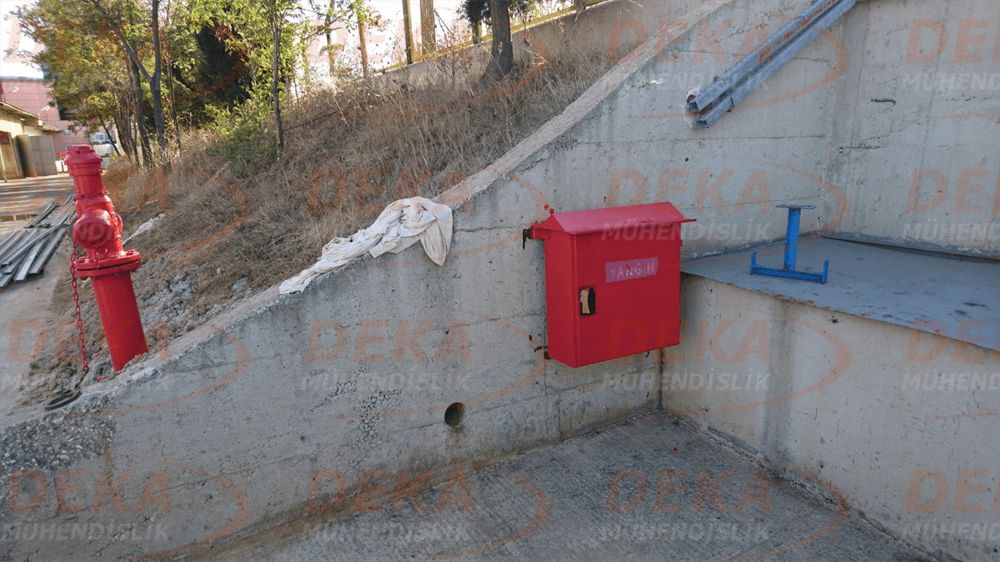
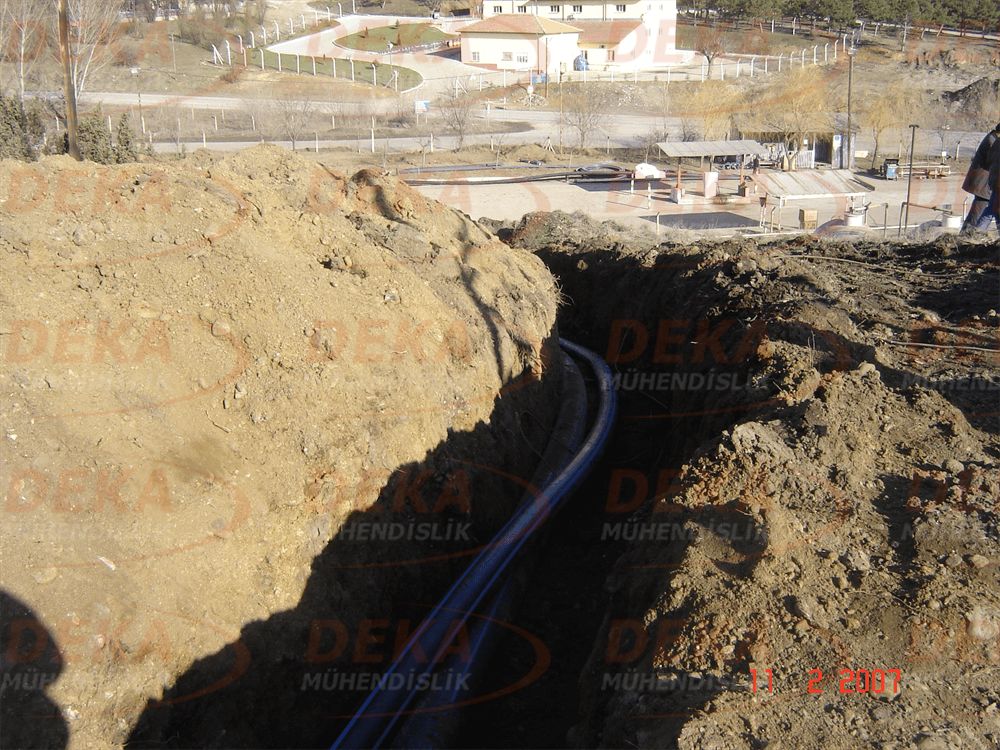
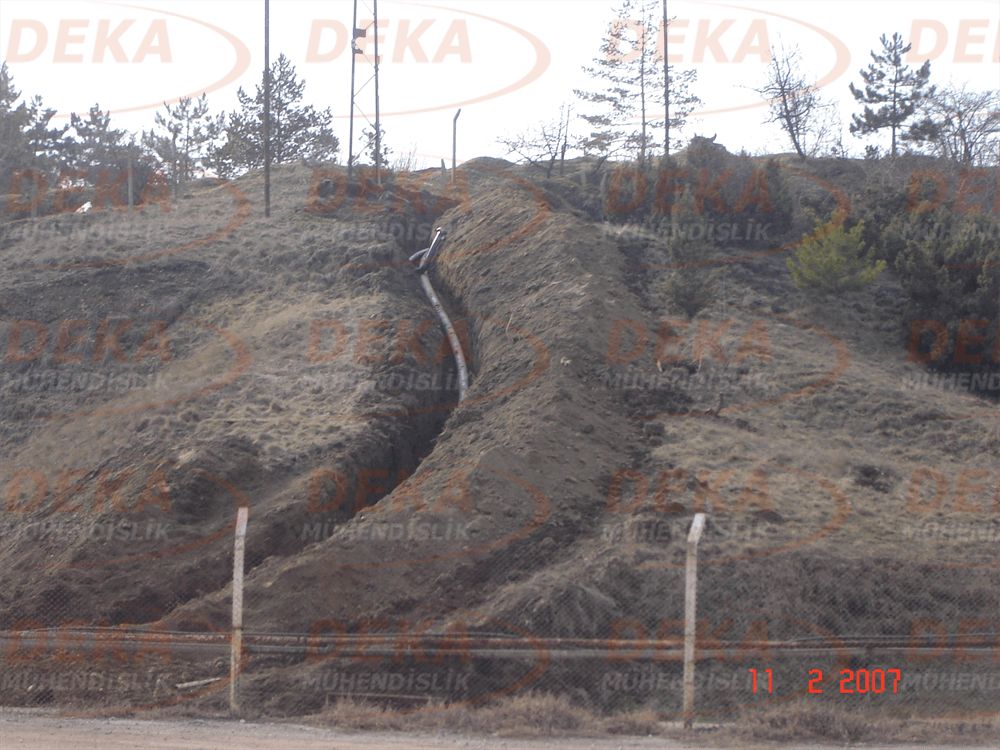
Hydrants should be surrounded by protection against external mechanical impacts and accidents. However, the application should not affect easy accessibility and usability. It will be useful to use direction and information signs to ensure the visibility and accessibility of fire hydrant places. In addition, by marking the route of the surrounding hydrant piping, it is ensured that the hydrant is separated from other under ground cables, pipelines and protected from work during possible excavation works.
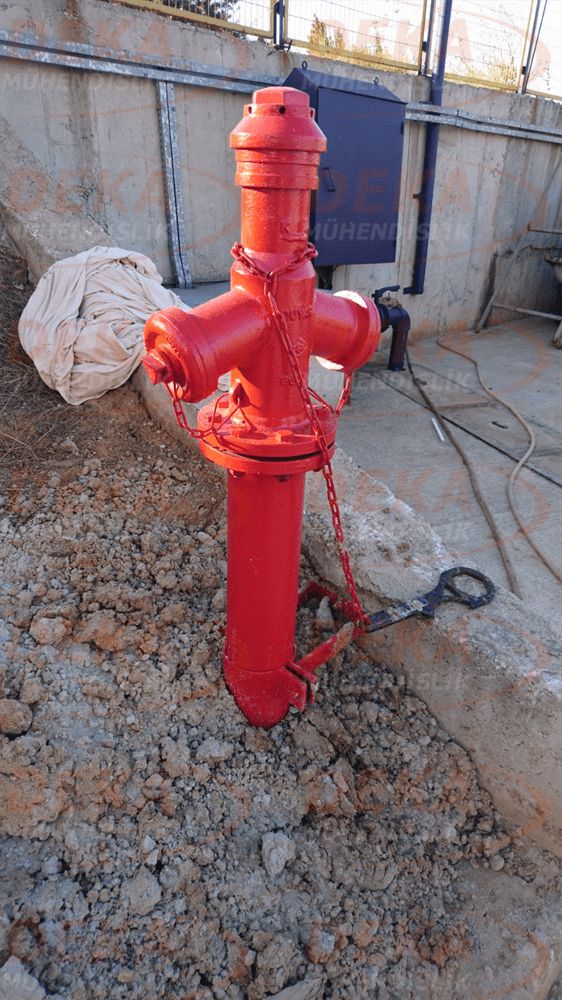
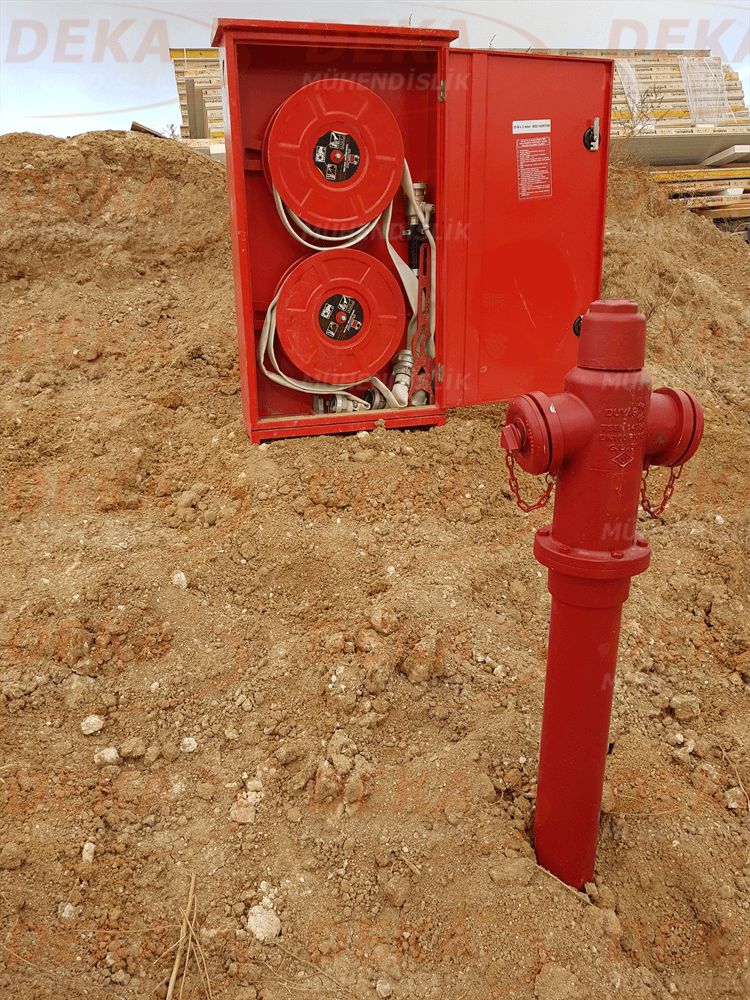
Aboveground fire hydrants; In addition to quick response to factories, warehouses, industrial facilities, building surroundings, forest lands and city settlements, it also enables the fire brigade to supply water.
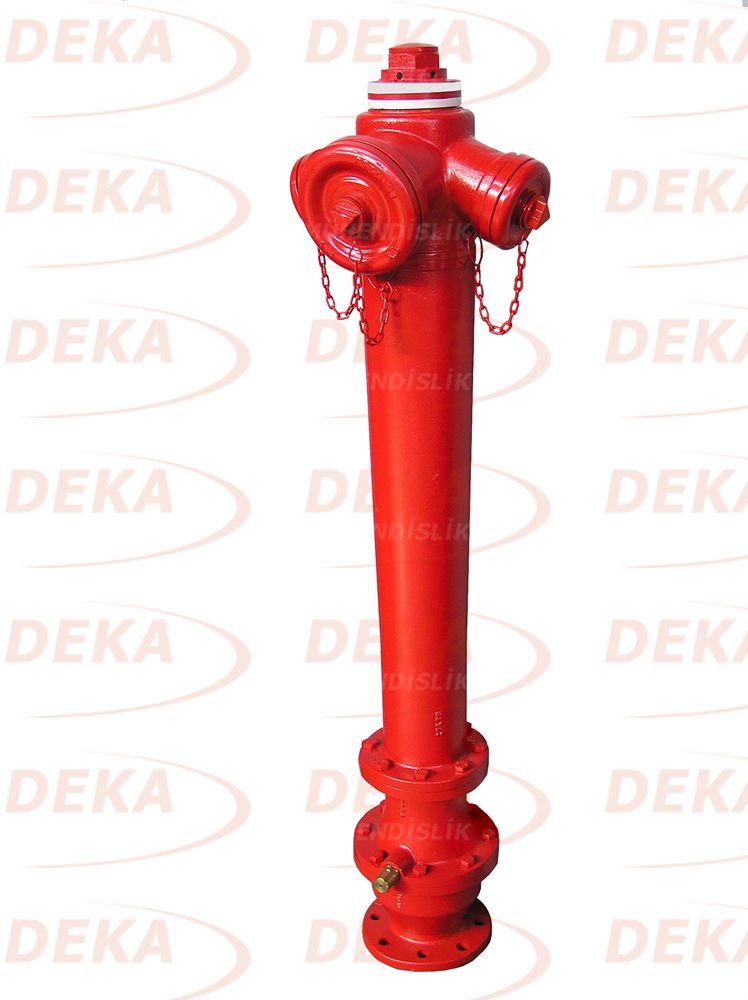
Aboveground fire hydrants are produced in various diameters depending on the place of use. There are DN80, DN100, DN150 diameters determined in TS2821 standards. Hydrant quenching capacity varies according to the inlet and outlet diameters. In general, there are two outputs DN65; There is a DN100 bottom outlet in DN100 nominal size hydrant and optional DN150 nominal size hydrants for fire trucks to get water quickly.
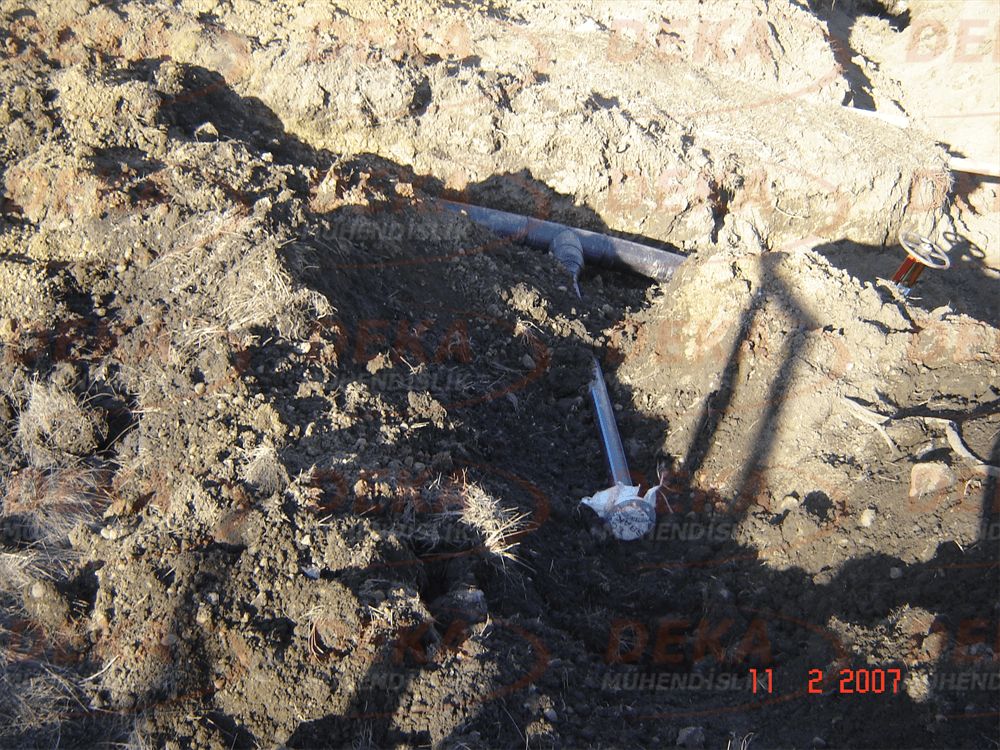
Unfortunately, due to improper and / or missing applications in the hydrant system, we are unfortunately faced with cracking in the pipes, deterioration of the composite structure and revision. In practice, it is important to use an impact block under the elbow and tee connections of the hydrant system. Hydrant elbow is not used, the plurality of fittings in deep hydrant lines and rigid connections cannot be provided, if the hydrant is on the surface, the hydrant discharge mouth stays on the ground and is affected by frost, the clogging caused by the application of gradual gravel in front of the hydrant discharge mouth and again, frost exposure, etc. situations are the most common application errors.
Fire hydrant is an indispensable and vital application applied outside the building. The right design, the right solution, the right application are important in order not to be an audience to the fire when the correct application is not made.